H13 Laser Sintering Process for Robust Tooling
Partnership is the key to developing advanced process parameters for producing robust H13 tooling using laser sintering process.
#toolsteel #conformalcooling
Working with Jason Murphy of Next Chapter Manufacturing to develop appropriate content for MoldMaking Technology’s niche audience lead me to Farsoon Technologies and how their partnership is helping to solve some additive tooling challenges.
Here is their story presented by the Farsoon team:
Featured Content
H13 is a widely used versatile tool steel and is well known for its excellent combination of high resistance to compression, thermal shock, and abrasion. Shops use H13 for more hot work tooling applications than other grades of tool steel as well as a variety of cold work conditions because of its high toughness and good stability in heat treatment. H13 covers a wide range of application from die casting, and extrusion dies and high toughness and polished (up to A1 grade) injection mold components.
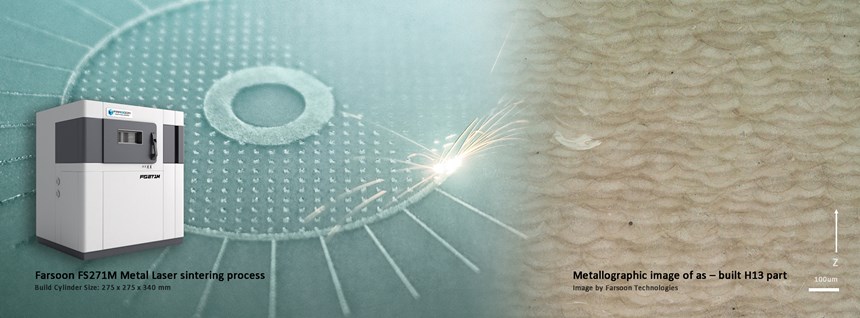
H13’s high carbon content makes it extremely difficult to weld or process with standard metal laser sintering parameters. The carbon content is easily vaporized and can contaminate the powder surface during the welding process, which may lead to internal flaws, and porosity and thermal cracks, especially in the areas of stress concentration.
To find the solution to the challenge, Farsoon’s application team partnered with Next Chapter Manufacturing in an ongoing program to develop advanced process parameters to produce robust H13 tooling using laser sintering process.
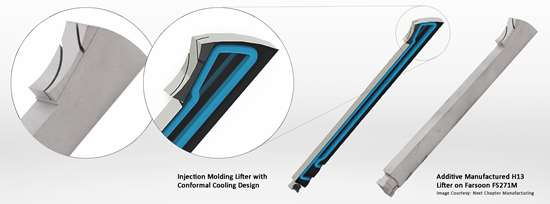
One example from this collaboration is a lifter used for cooling and separating the plastic parts from the core in injection mold production, which is employed in the internal undercut area with snaps and an enclosed shape. By adding a 1/16-inch NPT conformal water circuit design to the geometry of the lifter (Figure 1) and additively produced on a Farsoon FS271M system, Next Chapter Manufacturing was able to deliver four lifters in only eight days. The lifters can be directly installed in the factory system. The new conformal design helps accelerate the cooling process and eliminate the warpage in the finished part. The optimized lifters improved production volume with the original factory settings, reducing the cycle time from 48 seconds to only 30 seconds, and achieving an annual savings of $100,000.
“We decided to partner with Farsoon Technologies because its system is open, which means we can develop specific processes that enable us to print H13 and other tool steels efficiently,” Jason Murphy, president of Next Chapter Manufacturing says. “This open parameter system also enables us to do test builds and refine our process to improve robustness and speed further. The technology gives designers a significant amount of additional freedom to provide the most efficient designs for additive manufacturing, which other machines do not offer. “
Today, Farsoon’s application team has conducted a large number of tests to develop processing parameters including the laser power, scanning strategies, internal stress relieving as well as heat treating of parts using H13.
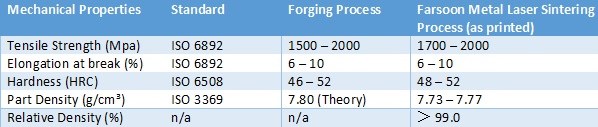
The optimized parameter set helps eliminate the thermal cracks when welding and delivering a high relative density of over 99.0 percent. The additively-produced H13 parts also showed mechanical properties that are fully comparable to wrought H13 material, achieving an as-built hardness of approximately 50 HRC. The as-sintered H13 part performance and open parameters offer users the freedom for further develop the process that is best tailored to their tooling applications.
RELATED CONTENT
-
Hot Runners and Valve Gate Systems: A Moldmaking Team
Valve gates provide several advantages when using hot runners, including better appearance, safety and an overall better product. There are several types of valve gates, and it is important to choose the right one for your project.
-
How to Choose the Right Tool Coating for Your Machining Application
Selection criteria and common coating attributes for PVD, CVD and other common coatings.
-
A Different Approach to Mold Venting
Alternative venting valves can help overcome standard mold venting limitations and improve mold performance.