Looking for a Tool Steel Heat Treatment Source?
How does agitating a quench liquid improve quenching speed? Why do tool steels require a high austenization temperature for hardending? How thick can a P20 mold steel be through hardened into the center? These and other questions were answered during last week's webinar on heat treatment basics.
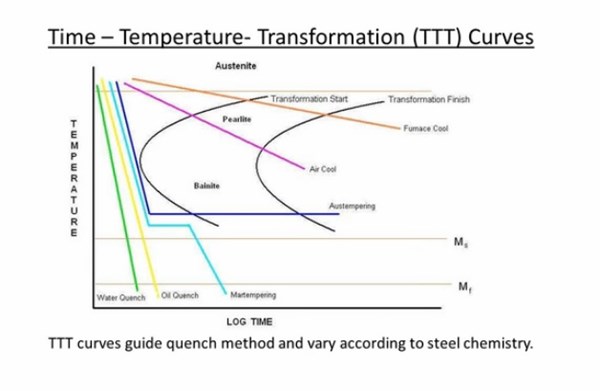
How does agitating a quench liquid improve quenching speed? Why do tool steels require a high austenization temperature for hardending? How thick can a P20 mold steel be through hardened into the center? These and other questions were answered during last week's webinar on heat treatment basics.
Mold and die steels can be supplied pre-hardened or in a soft condition to facilitate machining. If machined soft, the steel must be hardened to enable the material to withstand the demands of a production environment. Heat treatment is the process for hardening or altering the internal structure of steels. Several processes can be used to achieve the desired end condition. Once considered an art, heat treatment has been refined by science and technology to a reliable and repeatable industry.
Click here for our archived webinar presented by Ellwood Specialty Steel.
Related Content
-
Three Considerations for Mold Steel Selection
Although a big challenge is selecting the right steel for the right job, steel selection has never been better in regards to quality, price and delivery speed. Here is a simple checklist when selecting your next mold steel.
-
Modified Composition Enhances Stainless Steel Capabilities
Edro introduces Böhler’s M333 Isoplast stainless steel which has been manufactured via a new melting technology for best-in-class polishability, conductivity, toughness and corrosion resistance.
-
VIDEO: Qualifying Modified H-13 for 3D-Printed Tooling
Next Chapter Manufacturing and International Mold Steel discuss their partnership to qualify a modified H-13 for tooling applications.








_300x250 4.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)




