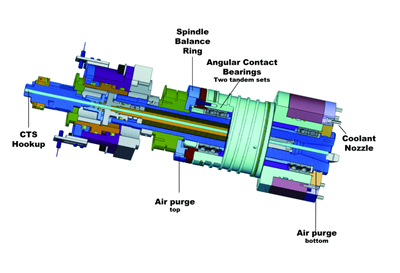
For mold work, a VMC offers the most effective design for machining complex shapes and surfaces. Spindle construction, thermal stability, and bed and column design are more important considerations than horsepower and torque. Source (All Images) | Hwacheon Machinery America Inc.
Speed, precision and stability are the key attributes of a mold machine. With the increased accuracy demanded by sophisticated molded assemblies, particularly in the automotive supplier industry, mold shaping machine tools continue to break new ground in precision, speed and multi-axis cutting.
For mold work, which typically takes light, high-precision cuts, a vertical machining center (VMC) offers the most effective design for machining complex shapes and surfaces. Spindle construction, thermal stability, and bed and column design are more important considerations than horsepower and torque. A mold machine should provide you a total production solution, from tool selection to final product.
Structure
Start at the heart of the machine tool: Structural stability is key to consistent precision machining. Typically created with finite element analysis (FEA) and CAD, the structure of the machine base and column are the foundation of machine stability. The design may be realized as weldments or in cast iron. Iron is arguably more effective at vibration dampening while offering superior stability.
Designed using 3D simulations and FEM analysis, leading machines are built for high structural rigidity, which can translate to quality product results and the elimination of hand-fitting of mold components.
A VMC for mold work should have a machine frame with a rigid bilateral gate structure, which firmly supports the X-axis drive and diverts load, vibration and heat from the upper section of the machine evenly throughout the frame. These features will help keep the feed drive stable after hours of operation. Also, the short distance between the X-axis drive and the tool’s point of contact will be a plus for maintaining rigidity and for enhancing machining precision.
Spindle = Speed
An integral spindle will provide outstanding performance in high-precision machining with the reduction of noise, vibration and heat. Because the high-speed motor is mounted directly on the assembled spindle shaft, there are no parts for transmission of power, resulting in reduced noise and vibration, minimal power loss and improved cutting efficiency.
Acceleration/deceleration time may be reduced as a result of a compact integral spindle, contributing to improved cycle times and surface finishes.
This large-capacity VMC can accommodate up to a 5,500-pound table load with 17 inches between columns. Smaller and mid-range machines are available.
A high-performance spindle, which integrates oil-jet cooling and lubrication technology will ensure consistent quality results after hours of operation. The oil-jet cooling and lubrication system injects a jet of oil directly onto the spindle bearing for effective cooling. The motor and spindle assembly are jacket-cooled to limit displacement caused by heat. Temperature is thus stabilized in a short time.
Software Suite
Another important consideration is the available suite of mold machining software components, which can positively impact the safety and the work efficiency of your organization and the quality of your output.
Thoughtfully designed machining software components will monitor different variables related to work environment and machining conditions, then make adjustments for high quality results and optimum machining efficiency. Software such as this would be specifically developed to increase thermal accuracy and machining performance.
Tool load detection software provides real-time measurement of tool load, ensuring consistent and safe machining. This software can ensure accuracy and performance by constantly monitoring tool damage and deterioration for prevention of complete tool failure that can cause workpiece damage. Such a system will measure tool load very frequently (e.g., every 8 milliseconds).
Start at the heart of the machine tool: Structural stability is key to consistent precision machining.
A contour control system will offer an easy-to-use programming interface that provides a precise, custom contour control for the selected workpiece while supporting longer machine life and reduced process time. Such software will offer different options for cutting speed and accuracy, and for surface finish and geometry. A customizable display can provide real-time monitoring and easy access. This software is able to be used with existing NC systems and is compatible with G-code programming.
A cutting feed optimization routine that utilizes an adaptive control method to regulate the feed rate in real time will sustain a consistent cutting load while machining. As a result, cutting tools are less prone to damage and machining time is reduced. This system controls the feed velocity to maintain consistent cutting load. Features to look for include a graphic display of tool load and feed rate, convenient operation using G-code programming and a number of data sets for specific tool and process control.
A gate structure firmly supports the X-axis drive and distributes the load, vibration and heat from the upper section of the machine evenly through the frame. This arrangement keeps the feed drive stable during operation
Another mold machine consideration are highly sensitive thermal sensors — mounted at various locations in the machine castings where thermal displacement is possible — that can permit software monitoring and correction of detected thermal displacement.
Spindle displacement control is also possible with the right software. As a spindle rotates at high speed, centrifugal forces and heat expand the spindle taper, causing error in the Z-axis. This axis accuracy is vital to precision mating of mold components. In addition to a high-precision cooled spindle, software can be used to constantly monitor temperature at a number of points within the spindle assembly, predicting thermal displacement. The system can then make necessary adjustments and effectively minimize thermal displacement, preventing Z-axis error due to taper expansion as the spindle rotates at high speed.
Toolholding
At any speed, a machine tool spindle is subject to centrifugal forces that increase as speed increases. At high speed, centrifugal force is strong enough to make a spindle bore grow slightly. As a collet segment rotates, the clamping mechanism gains centrifugal force and causes the relatively thin walls of the tapered shank to deflect radially at a faster rate than the wall of the spindle. This contributes to a stronger contact between the shank and the spindle, without affecting the axial position of the cutting edge, as it is determined by the face-to-face contact between the flange and the receiver.
An HSK toolholder has contact on the spindle face and taper. When the spindle begins to grow, the face contact prevents the tool from moving up the bore.
Most commonly, shrink-fit toolholders are used in mold machining due to total contact between tool and holder, approximating a solid carbide tool. This avoids the effects of temperature and vibration on the tool, supporting machining precision and high-quality mold surfaces.
Summary
A well-designed mold machining center with an optimal machining system — including spindle, software frame and toolholders — delivers a total production method from tool selection to final product and provides the best choice for high-precision applications of various types and materials.
Related Content
Laser Welding Versus Micro Welding
The latest battle in finely detailed restoration/repair of mold materials.
Read MoreSolving Mold Alignment Problems with the Right Alignment Lock
Correct alignment lock selection can reduce maintenance costs and molding downtime, as well as increase part quality over the mold’s entire life.
Read MoreConsiderations for Mold Base Material Selection
Choosing the right material can greatly affect the profitability and cost of your application.
Read MoreHands-on Workshop Teaches Mold Maintenance Process
Intensive workshop teaches the process of mold maintenance to help put an end to the firefighting culture of many toolrooms.
Read MoreRead Next
Machining Center Spindles: What You Need to Know
Why and how to research spindle technology before purchasing a machining center.
Read MoreWhy Your Next VMC Should Be a HMC
High technology raises the bar for productivity gains.
Read More










.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)