Wear Parts and Consumables: The Keys to Maximizing Your EDM
Mold shops need to pay attention to the potential impact wear parts and consumables can have on their overall production.
As global competition has caused manufacturers to raise the bar for machine performance and productivity, many have realized the importance of proper maintenance when it comes to maximizing a machine’s effectiveness. Far fewer have recognized the potential impact of wear parts and consumables on overall production.
With current technology, consumable parts can play a critical role in the overall success of a machine investment. Similar to the way inexpensive tires can eliminate the benefits of a high-performance automobile, low quality consumables can result in subpar machine performance. This holds especially true when talking about wire EDM.
To demonstrate the effects of maintenance and using the correct consumables and wear parts, a test piece was cut on 40 wire EDMs across the country. With a median age of eight years, all of the machines underwent a preventative maintenance program using original parts. After cutting with a .010” wire for one rough and two skim cuts, measurement of the finished test parts revealed the median deviation was a mere .00015”. Regardless of age, the cutting time for all machines was exactly the same as it had been when they were new from the factory, demonstrating the potential power of maintenance and using manufacturers’ recommended consumables and wear parts.
Wires
Perhaps the most obvious consumable to affect wire EDM performance is the wire itself. A great deal of EDM users have switched to inexpensive wires in an effort to save money. While these options might meet an operation’s minimum standards, they often leave much to be desired. To truly maximize cutting performance without wire breakage or sacrifices in accuracy or surface finish, users should select wire based on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
In most cases, machine builders work together with wire manufacturers to develop new wires and cutting technologies that maximize the performance of each machine’s specific spark generator. Additionally, different wire materials perform at varying levels in different situations. Coated wires typically excel when fast cutting and high accuracy are required. For applications with tapers over 15 degrees, the best choice will most likely be a soft brass wire or coated wire with high elongation. These types of suggestions can often be obtained through a machine’s CNC or Expert system. A manufacturer’s application department also should be able to provide advice on which wire to use for a specific job.
For those looking to maximize cost savings on EDM wire, twin wire technology provides the ability to rough cut with a coated wire for maximum cutting speed and then switch to a less expensive brass wire for finishing. Tests have demonstrated that twin wire EDMs can increase production by 15 percent without increasing wire costs.
Wire Guides
An EDM’s wire guides are usually the most important components for cutting highly accurate parts. With closed wire guides, the clearance between the wire and the opening in the guide will greatly influence the machine’s ability to cut accurately, especially where tapers are concerned. The exterior of a wire guide is composed of either stainless steel or ceramics, with a PCD (polycrystalline diamond) interior, as this material is extremely hard and wears very slowly. If a cross section of a high quality wire guide were to be examined, one would observe a radius on its inside. A high quality radius results in less friction on the wire and also provides higher surface finish and accuracy when cutting large tapers between 30 and 40 degrees.
Power Contacts
Once the correct wire and guides have been selected, it is important to choose the correct power contacts for a wire EDM. These components ensure the proper transfer of energy from the spark generator to the wire. The geometry of these parts determines whether they achieve the correct amount of surface contact with the wire. This, in turn, affects both the wear rate of the contact and cutting speed of the machine. The wrong power contacts can have a very negative effect on overall cutting speed. Between this loss in productivity, sacrifices in accuracy and surface finish, and the shortened life associated with cheaper versions of the power contacts, the option that is least expensive upfront often proves to cost more in the long term.
On a similar note, the power cable connected to the work table also influences machine performance. These cables need to have the right diameter and length, and must be manufactured from the proper copper alloy to guarantee optimal cutting performance.
Flushing Nozzles
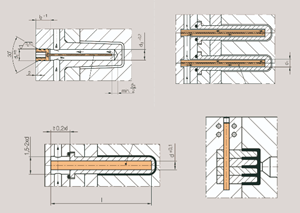
Flushing nozzles also provide a clear example of how wear items can influence the cutting speed of a machine. To the naked eye, the external view of aftermarket flushing nozzles may appear nearly identical to a manufacturer’s original parts. However, the unseen interior design greatly influences the flow of water (Figure 1, page 19). A proper flow is vital to delivering water to the cutting zone without creating air bubbles or other turbulences that cause wire breakage and decreased cutting speeds. With non-submerged machines, the flushing nozzle is even more critical. During the skim cut, an interruption to the water surrounding the wire can cause red sparks that create lines on the part. A smooth and consistent column of water around the wire eliminates this risk.
Water Filters
Water filters also play an important role in getting the most out of a wire EDM. Filters need to be the correct size to achieve adequate flushing pressure, and also must be properly designed to keep EDM particles from being brought back into the cutting zone. In most cases, this means using an 8 to 10 micron filter for general flushing and a 5 micron filter for threading jet filtration. Some original manufacturers’ filters have additional surface inside the filter that increases performance and life by up to 2.5 times in some cases. This can make a significant difference in the amount of time spent on filter changes, along with reducing costs beyond what would be achievable with a cheaper filter.
Automatic Wire Threading System and Knives
For those wishing to run their wire EDM unattended, an automatic wire threading system is a necessity. One such system—a high-speed and maintenance-free wire threading system that stretches the wire and cuts it under the effect of heat, regardless of wire diameter and material—accomplishes this without moving parts and only one consumable component, the diffuser guiding the water jet. An additional no-threading-hole detection feature prevents the machine from shutting down, which is especially critical during unattended machining.
In older machines, though, knives in the upper head constitute another consumable to be considered. These parts are critical to obtaining a precise cut of the wire without creating a burr, which could prevent the wire from threading correctly. The knives used in automatic wire threading systems are typically found as carbide or ceramic parts. Of these two options, ceramic parts last longer, which can justify their slightly higher cost to those who wish to run lights out through extended periods of time.
Getting the Most Out of Your EDM
As with any large investment, companies often pay great attention to the quality of a machine they are about to purchase. Too often though, little attention is paid to the consumable parts that will be used in the machine’s day-to-day operations. Those mold manufacturers who focus on using the best-suited consumables will find themselves getting far more out of their machines than would otherwise be possible. It is these types of advantages that help U.S. manufacturers compete in today’s global marketplace.
Related Content
Fundamentals of Designing the Optimal Cooling System
The right mold components can help improve mold cooling and thereby produce higher-quality parts.
Read More6 Ways to Optimize High-Feed Milling
High-feed milling can significantly outweigh potential reliability challenges. Consider these six strategies in order to make high-feed milling successful for your business.
Read MoreHow to Eliminate Chatter
Here are techniques commonly used to combat chatter and guidelines to establish a foundation for optimizing the moldmaking process.
Read MorePlastic Prototypes Using Silicone Rubber Molds
How-to, step-by-step instructions that take you from making the master pattern to making the mold and casting the plastic parts.
Read MoreRead Next
How to Implement Ultra Productive EDM
Steps to help maximize the potential of your current die sink or wire EDM system.
Read MoreReasons to Use Fiber Lasers for Mold Cleaning
Fiber lasers offer a simplicity, speed, control and portability, minimizing mold cleaning risks.
Read MoreHow to Use Strategic Planning Tools, Data to Manage the Human Side of Business
Q&A with Marion Wells, MMT EAB member and founder of Human Asset Management.
Read More















.jpg;maxWidth=300;quality=90)



_300x250 4.png;maxWidth=300;quality=90)